What Are Tariffs? Impact of Recent U.S. Tariffs on Global Trade

tariffs
global tariffs
EU zero for zero deal
WTO trade
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported goods. Its primary purpose is to make foreign products more expensive, thereby encouraging consumers to buy domestic products. Tariffs are often used to protect local industries, balance trade deficits, and sometimes even as a political tool.
🏛️ Introduction: What is a Tariff?
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported goods. Its primary purpose is to make foreign products more expensive, thereby encouraging consumers to buy domestic products. Tariffs are often used to protect local industries, balance trade deficits, and sometimes even as a political tool.
🌎 Why Do Countries Use Tariffs?
Governments use tariffs for several key reasons:
🛡️ Protect Domestic Industries: Tariffs make foreign goods more expensive, so consumers are more likely to buy locally-made products.
💰 Raise Government Revenue: Especially in developing countries, tariffs are a major source of income.
⚖️ Correct Trade Imbalances: If one country imports much more than it exports, it may impose tariffs to level the trade flow.
💼 Retaliate in Trade Disputes: Tariffs are often used as a weapon in trade wars to retaliate against other countries' trade policies.
🔐 Enhance National Security: Some tariffs aim to reduce dependence on other countries for critical goods (like energy, food, or medicine).
Tariffs are not just economic tools — they often have political motives behind them, too.
🧾 Types of Tariffs
- Ad Valorem Tariff: A percentage of the value of the good (e.g., 10% on a $1,000 product = $100 tariff)
- Specific Tariff: A fixed fee per unit (e.g., $2 per liter of imported wine)
- Compound Tariff: Combines both ad valorem and specific tariffs (e.g., 5% + $1 per item).
📌 In Simple Words: A tariff is like a tax added to foreign goods to make them cost more, protect local jobs, or settle political arguments.
US Recent U.S. Tariffs: What Happened?
In recent years, the U.S. government has imposed tariffs on countries like China, Mexico, Canada, and EU nations — especially in sectors like steel, aluminum, electronics, and automotive parts.
Some key actions include:
- 2025 Tariffs on Chinese imports increased to 145%, citing national security concerns.
- 25% tariffs on all imports from Mexico and Canada, excluding Canadian oil and energy, which are taxed at 10%.
- 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum imports, affecting global supply chains.
China's Response to U.S. Tariffs
China has implemented several countermeasures in response to U.S. tariffs:
- Raised tariffs on U.S. goods from 84% to 125%, affecting various sectors.
- Imposed additional tariffs of 10-15% on U.S. energy products, including coal, LNG, and crude oil.
- Expanded export controls on critical minerals, such as tungsten, tellurium, bismuth, molybdenum, and indium.
- Launched antitrust investigations into U.S. companies, including Google.
- Filed complaints with the World Trade Organization (WTO), challenging the legality of U.S. tariff measures.
📊 How Do Tariffs Impact Global Trade?
- Increased product costs: Tariffs raise the prices of imported goods, leading to higher costs for consumers and businesses.
- Disrupted supply chains: Companies may need to find alternative suppliers or relocate production to avoid tariffs.
- Trade tensions and retaliatory tariffs: Countries may impose their own tariffs, leading to a cycle of retaliation.
- Market volatility: Uncertainty surrounding trade policies can lead to fluctuations in financial markets
🌍 Global Impact and Other Countries' Reactions
The escalating trade tensions between the U.S. and China have had ripple effects worldwide:
- Canada and Mexico: Implemented retaliatory tariffs on U.S. goods in response to U.S. tariffs.
- European Union: Expressed concerns over the potential for a global trade war and is exploring measures to protect its industries.
- Developing Nations: Countries like India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh are navigating the shifting trade dynamics, with some benefiting from supply chain realignments.
📈 Impact on U.S. Consumers and Businesses
- Higher prices for imported goods
- Increased costs for manufacturers who rely on global supply chains
- Reduced exports due to retaliation
- Uncertainty for investors and markets
🧠 Economic & Political Perspective
Tariffs can help protect industries temporarily, but long-term protectionism often leads to inefficiency, reduced competition, and economic friction.
Global tariff wars in 2025

global tariff wars in 2025 countries
U.S. Tariff Overview (as of April 2025)
- Universal Import Tariff: 10% on all imports (effective April 5, 2025)Wikipedia
- Higher Country-Specific Tariffs: Applied to approximately 60 countries based on trade deficits and perceived unfair practices (effective April 9, 2025)Wikipedia+1Wikipedia+1
- China: 54% effective tariff rate after combining new and existing levies
Recent U.S. tariffs on other countries
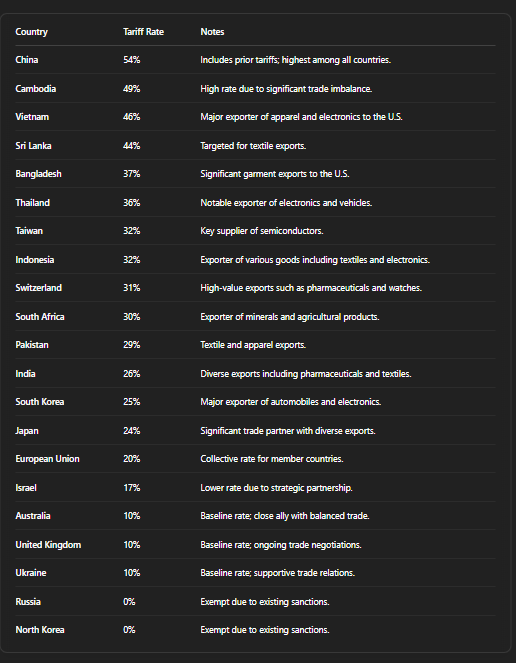
tariff list about US
Note: Tariffs on steel, aluminum, vehicles, and vehicle parts remain unchanged from previous measures. Energy products and certain minerals not available in the U.S. are exempted.Wikipedia
📦 Product Categories Affected
- Apparel and Footwear: Countries like Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Cambodia face high tariffs, impacting clothing and shoe prices.CBS News
- Electronics and Semiconductors: Tariffs on Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan affect consumer electronics and components.
- Automobiles and Parts: Higher tariffs on Japan and South Korea impact vehicle imports.Wikipedia
- Agricultural Products: Tariffs on countries like South Africa and Thailand affect fruit, nuts, and other imports.
- Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals: Switzerland and India face tariffs affecting drug and chemical imports.
🔍 Additional Measures
- De Minimis Threshold Elimination: The $800 duty-free import threshold for China was removed effective May 2, 2025, with plans to extend this to other countries, increasing costs for direct-to-consumer imports.Wikipedia
